Introduction:
Stem cell banking has emerged as a transformative medical practice, offering families a proactive means of securing their loved ones’ health and well-being. By preserving the valuable stem cells found in various sources, such as umbilical cord blood and tissue, bone marrow, and adipose tissue, this forward-thinking approach holds immense potential for treating a wide range of diseases and medical conditions. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the significance of stem cell banking, explore the wonders of stem cells, and shed light on the remarkable benefits it offers. Discover how this decision can empower your family with the gift of a healthier and more resilient future.
1: Understanding Stem Cell Banking
Stem cell banking involves the collection, processing, and cryopreservation of stem cells from different sources. These cells are the body’s natural building blocks, capable of differentiating into specialized cells and promoting tissue repair and regeneration.
2: The Marvels of Stem Cells
Stem cells possess unique regenerative properties that make them invaluable in modern medicine. Their ability to repair damaged tissues and treat various diseases has revolutionized medical treatments and opened new avenues for research.
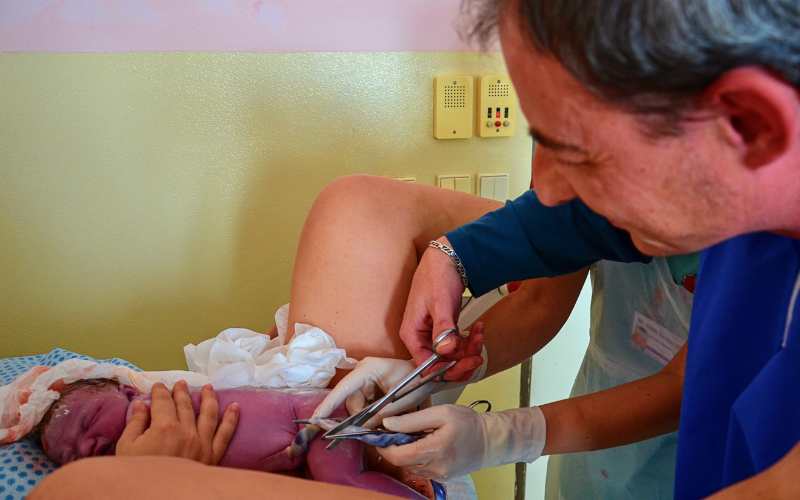
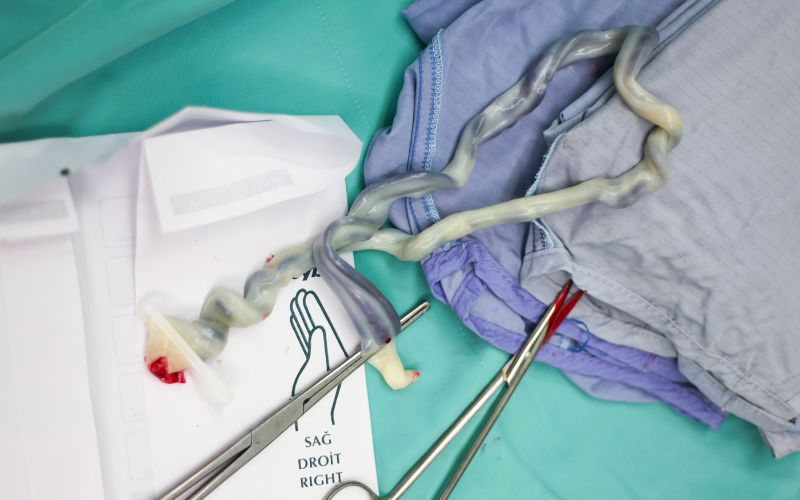
3: Umbilical Cord Blood and Tissue Banking
Umbilical cord blood and tissue banking is a widely practiced form of stem cell banking. The stem cells obtained from the umbilical cord are particularly rich and versatile, making them an excellent resource for potential future medical use.
4: Bone Marrow and Adipose Tissue Banking
Bone marrow and adipose tissue also serve as valuable sources of stem cells. Bone marrow stem cells are commonly used in treating blood-related disorders, while adipose tissue provides a readily available and abundant source of mesenchymal stem cells.
5: The Wide Range of Medical Applications
Stem cell banking offers a wide range of medical applications. From treating leukemia and other blood disorders to regenerative therapies for conditions like spinal cord injuries and heart disease, the potential uses of banked stem cells are diverse and promising.
6: Benefits for Immediate and Extended Family
Stem cell banking not only benefits the individual but also extends to immediate family members. Siblings and parents who share a genetic match with the banked stem cells may also benefit from potential treatments in the future.
7: Personalized and Regenerative Medicine
Stem cell banking plays a pivotal role in the advancement of personalized and regenerative medicine. By providing a genetically compatible source of stem cells, banking enables tailored treatments for specific individuals, increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
8: The Role of Stem Cell Banking in Medical Research
Banked stem cells significantly contribute to medical research. Researchers can use these cells to study diseases, test new therapies, and gain a deeper understanding of stem cell biology, driving advancements in healthcare.
9: Making an Informed Decision: Guidance and Resources
Making the decision to pursue stem cell banking requires thoughtful consideration. This section provides guidance on the various sources of stem cells, the banking process, and selecting a reputable stem cell bank for your family’s needs.
Conclusion:
Stem cell banking offers families a proactive investment in their health and future. By preserving the remarkable potential of stem cells, you are providing a powerful resource that may pave the way for future medical breakthroughs and treatments. Consider the diverse medical applications, the benefits for immediate and extended family members, and the contribution to scientific research. Embrace this decision as a symbol of hope and preparedness, knowing that you have taken a significant step towards securing a healthier and more resilient future for your loved ones. With the promise of science and the boundless potential of stem cells, stem cell banking empowers families to embrace a brighter tomorrow filled with possibilities.